Has your ankle ever been turned round and swollen like a balloon? Or wake up with swollen, weird eyes? You are on your feet all day, and your feet feel like they have grown a size. This uncomfortable, alarming puffiness has a name, and it is swelling. It is your body’s natural, but annoying, response to something being wrong. From small bumps to indications of a serious health problem, it is important to be aware of this common response in order to make the correct choice. You can find plain language instructions on the tips and tricks to use in swelling remedies, or hints as to when to consult the doctor, in this guide.
Table of Contents
What is Swelling?
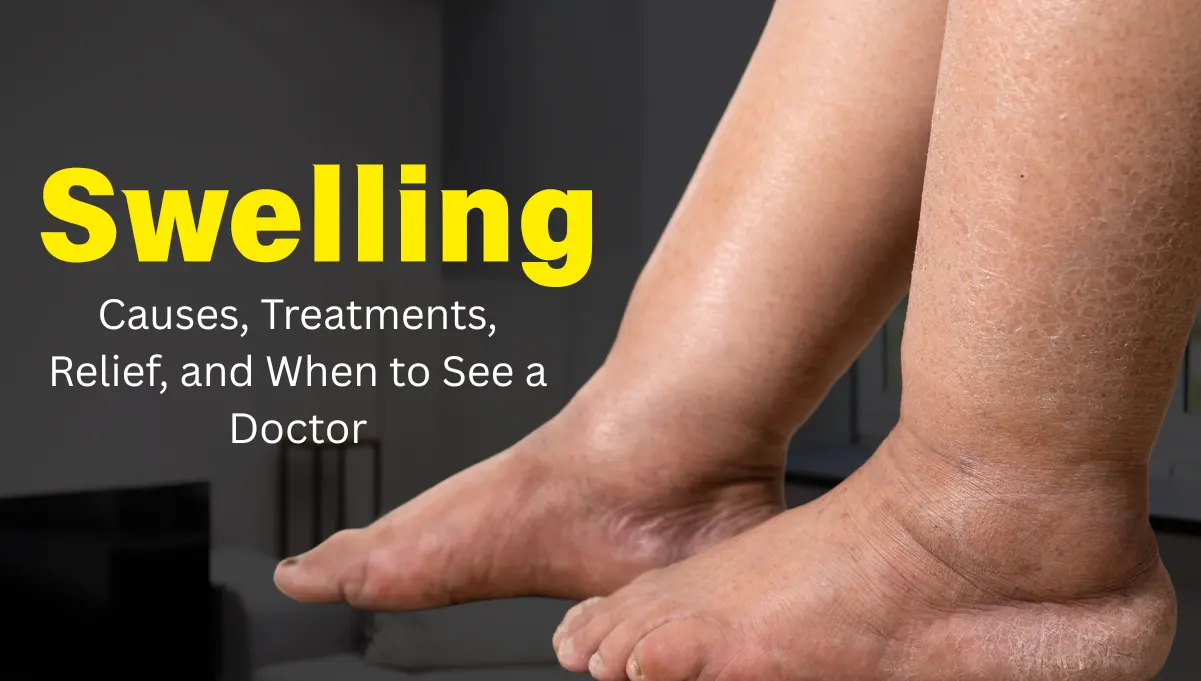
Simple puffiness (also known as swelling) is nothing more than your body experiencing retention of excess fluid in the body tissues. Suppose you take your skin and the muscles and pretend they were a sponge saturated with too much water. This normally occurs during the process of inflammation, which is the process of normal repair by your body. Once a sprain occurs, e.g., it dispatches fluid and white blood cells to the location to initiate healing. Swelling may be localized (it may be in a single location, such as a swollen ankle) or generalized (it may be spread all over the body), and it may be benign, a temporary annoyance, or prognostic of an underlying cause.
Swelling Symptoms
It is possible to identify the symptoms of swelling early on and, in that way, react more quickly. Look out for:
- Observable Changes: The area appears to be bigger or puffy. The skin can be tight, shiny, or stretched.
- Physical Sensations: Intentionally, the location is usually tender, warm, itchy, or painful. You may observe a depression, which lasts for seconds after pressing it (referred to as boring swelling).
- Functional Limits: Sometimes the swelling may make it difficult to move around a joint, especially due to stiffness. An eye that is swollen, as an illustration, may cause your eyelids to be excessively heavy and hard to open fully.
- Internal Signals: Occasionally, there are systemic symptoms in the form of unexplained weight gain over days, a feeling of fullness, nausea, or a sense of general malaise evident in the body, despite the fact that there is no swollen edge.
Swelling Causes
Why does it happen? The stimuli include broad ones:
- Damages to Tissues & Local: Sprains, fractures, burns, insect bites, and infections (such as cellulitis) determine fluid rushing towards the injured part.
- Lifestyle & Environment: Sitting or standing, salty foods, hot climate, and hormonal changes (such as pregnancy or menstruation period) may cause fluid retention.
- Allergic Reactions: This may involve mild rashes to severe anaphylaxis, which may result in the swift swelling of any of these areas: face, lips, or throat.
- Background Health Conditions: This is where one will have to look into. Problems with the heart, kidney, or liver. These may cause the body to fail to control the amount of fluids, therefore causing general swelling. Some blood pressure medications or diabetes may also be one of the contributors.
Treatment of Swelling
In the majority of minor acute swellings, home swelling management is the beginning of success. Use the following technique to decrease body swelling;
- Precepts of the PRICE Protocol: In cases of injuries, Protection, Rest, Ice (twice towels wrap ice with a towel, get 15-20 minutes on top of one another), Compression (elastic bandage), and Elevation (elevate the level of the area above the heart).
- Lifestyle Change: Minimize salt in the diet, hydrate, exercise regularly in a soothing manner to improve blood flow, and use compression stockings to prevent swelling of the legs.
- Ingenious Uses of Medicine: Anti-inflammatory medications can be used (irrespective of age) as over-the-counter pain killers (such as ibuprofen). Due to certain reasons, a physician can prescribe swelling medication such as diuretics or antihistamines due to allergies (so-called water pills to retain fluid or antihistamines). Medication should never be taken outside of instructions and ideally not without the guidance of a doctor.
When to Seek a Doctor for Swelling
The majority of the mild swelling could be resolved by rest, pressure, and time. However, the following red flags are the reasons why it is time to visit a doctor or even the emergency room:
- Swelling, which occurs suddenly, is extremely painful, and its cause is not clear.
- Edema (or a single leg), that is, with redness, warmth, or pain (may have a blood clot).
- Puffing of the eye, which brings about vision alteration, extreme pain, or fever.
- Puffy with dyspnea, aches in the chest, light-headedness or dizziness, or distraction.
- Edema, which does not subside after several days of home treatment, or rather continues to worsen.
- Swelling and fever, lower urine, skin that is yellowish, or a terribly swollen abdomen.
- Roughness in a person who is diabetic, heart, kidney, and liver diseases.
You must be logged in to post a comment.