Appendicitis is one of the most common medical emergencies that should be treated immediately. It is a disorder that arises due to the swelling or inflammation of the appendix, a small and tube-shaped pouch to which the large intestine is attached. Appendicitis may begin with some mild pain in the abdomen, but in a short period, the rate of progression may increase and, in a short time, lead to severe and life-threatening complications without timely treatment. The awareness of the 4 stages of appendicitis enables people to diagnose the symptoms promptly, receive medical treatment on time, and avoid complications associated with rupture or peritonitis.
We are going to discuss the 4 stages of appendicitis, the progression of this condition, its causes, risk factors, complications, diagnosis, and the treatment options in this blog.
Table of Contents
Know About Appendicitis
Appendicitis refers to inflammation of the Appendix. The lumen of the appendix is obstructed when the appendix is blocked (e.g. by stool, infection, or a foreign body). This blockage leads to swelling, bacteria overgrowth and inflammation which after failing to be treated in time may deteriorate over time.
Types of Appendicitis
Appendicitis can be broadly categorized into two types:
1. Acute Appendicitis
- Sudden onset
- Severe and intense symptoms
- Requires emergency surgery
2. Chronic Appendicitis
- Less common
- The recurrence of symptoms is non-persistent.
- Not an emergency, not a medical emergency but emergency-needed to be removed by surgery.
Acute Appendicitis vs Chronic Appendicitis
| Feature | Acute Appendicitis | Chronic Appendicitis |
|---|---|---|
| Onset | Sudden | Gradual, intermittent |
| Severity | Severe, intense pain | Mild to moderate symptoms |
| Treatment | Immediate appendectomy | Appendectomy usually required |
| Urgency | Medical emergency | Less urgent but important |
Common Causes of Appendicitis
Appendicitis can be triggered by a number of factors, which include:
1. Fecaliths (Hardened Stool)
Most prevalent cause; occludes the orifice of the appendix.
2. Follicles of the Lymphoid Tissue
In many cases, caused by infection of other parts of the body.
3. Foreign Bodies
Blockage may be caused by rare, but accidental ingestion.
4. Gastrointestinal Infections
May lead to increase in the size of tissues of the appendix.
5. Tumors
Rare, but may occur; may block the lumen of the appendix.
6. General Obstruction
Any hindrance predisposes to infection and inflammation.
Risk Factors of Appendicitis
The following are factors that make one prone to develop appendicitis:
Age
Most common between 10 to 30 years.
Gender
A little bit more prevalent in men.
Genetic Predisposition
Risk is augmented by family history.
Past Abdominal Surgery
The scar tissue or adhesions can block the appendix.
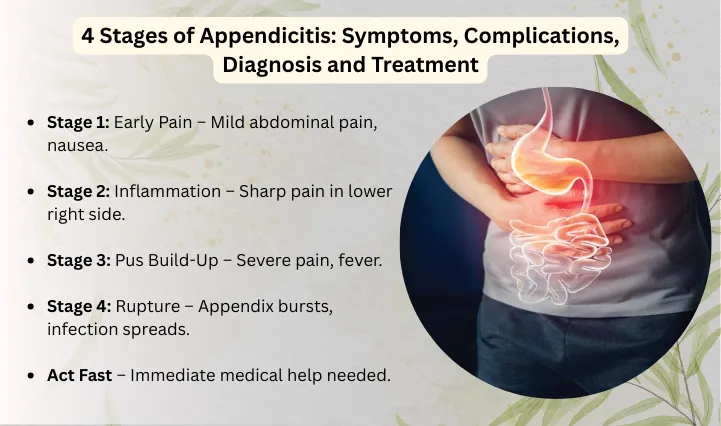
What Are the 4 Stages of Appendicitis?
There are 4 stages of appendicitis that are characterized by a gradual rise of inflammation, pain, and risk. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment would go a long way in turning things around.
Appendicitis has 4 stages, which are:
- Catarrhal Appendicitis (Early Inflammation).
- Suppurative Stage (Pus Formation)
- Gangrenous Appendix
- Sublaconic Rupture (perforated appendix).
We will discuss each of the stages separately.
1. Early Stage of Appendicitis: Inflammation
The first step in appendicitis is the obstruction of the opening of the appendix which results in the swelling, irritation and the growth of bacteria.
What Happens in This Stage?
- Mild inflammation starts in the appendix.
- The lumen of the appendices is blocked by the feces (fecalith), the swelling of the lymph node, or any other factors.
- The pressure slowly accumulates in the appendix.
Symptoms
- Abdominal pain, dull, perinumbinal.
- Sensation slowly changes to lower right abdomen.
- Mild nausea
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue or discomfort
Read More About – Zika Virus Symptoms: Early Signs, Stages, Causes and More
Why Early Detection Matters?
The early identification of the symptoms in this stage enables the doctors to make a diagnosis of the condition before complications set in. Early inflammatory treatment would result in a faster recovery process and stop further deterioration of the appendix.
2. Suppurative Appendicitis (Formation of Pus)
When inflammation advances, the appendix starts secretion of pus, which is the second stage of inflammation called suppurative appendicitis.
What Happens at This Stage?
- Infection of bacteria is aggravated.
- The appendix fills with pus.
- There is an exponential rise in pressure and swelling.
Symptoms
- Pain is sharp, persistent; localized in the right lower abdomen.
- Fever
- Vomiting
- Nausea
- Increased white blood cell count.
- Generalized unwell feeling
Medical Importance
This phase needs immediate medical care which is normally a surgical procedure. The appendix can also evolve to the gangrenous stage without treatment, lacking its blood supply.
3. Gangrenous Appendix
The third phase is the most important with pre-rupture. The inflamed appendix loses the supply of blood, which makes it gangrenous.
What Happens?
- Necrosis of the tissues starts.
- The circulation of blood is impaired.
- The appendix starts to rot internally.
Symptoms
- Excessive, intolerable pain in the abdomen.
- Persistent fever
- Rapid heartbeat
- Distended abdomen
- Signs of systemic infection
Why It’s Dangerous?
There is a gangrenous appendix, which is about to burst (perforation). Surgery is urgent to avoid the spread of the infection to the abdominal cavity.
4. Perforated Appendix (Rupture) -The Dangerous Stage
This is the progressive and the most serious phase of appendicitis. Once the appendix is not able to handle the pressure, it bursts.
What Happens After Rupture?
- The appendix ruptures giving pus and infectious contents outside the appendix.
- The spread of infection occurs all over the abdomen leading to peritonitis.
- Abscesses (cavities of pus) can develop.
Symptoms
- Immediacy relieving pain (transient) and then:
- Egregious, far-reaching stomachache.
- Very high fever
- Rigid or board-like abdomen
- Rapid breathing
- Confusion or weakness
Complications at This Stage
- Sepsis
- Peritonitis
- Abdominal abscess
- Life-threatening infection
Other Phases That May Be Observed in Appendicitis
Other variations may exist besides the traditional 4 stages of appendicitis including:
Phlegmonous Appendicitis
- A ruptured or inflamed appendix is encircled by omentum or loops of bowel to form a phlegmon (inflammatory mass).
- Appendicular Abscess
- An appendage localized pocket of pus develops.
Appendicitis Resolving Spontaneously.
In the long run, the obstruction resolves, and the symptoms disappear.
Recurrent Appendicitis
The symptoms reappear after periods of remission; approximately ten percent of all patients develop this.
Complications of Appendicitis
When appendicitis is not treated, it becomes possible to get complications within a short period of time:
1. Ischemia and Necrosis
Reduction in the supply of blood leads to tissue death.
2. Gangrene and Perforation
Dead tissue causes rupture.
3. Abscess Formation
Pus collection in the surrounding of the appendix.
4. Peritonitis
The infection spreads to the abdominal cavity; it is life-threatening.
5. Sepsis and Septic Shock
Bacteria enter bloodstream → emergency situation.
Diagnosis of Appendicitis
Healthcare providers rely on:
Physical Examination
- Examining rebound tenderness.
- Abdominal stiffness
- Guarding reflex
Blood Test
High WBC level is an indicator of infection.
Urine Test
Rules out kidney stones and UTI.
Imaging Tests
- Abdominal ultrasound
- CT scan
- MRI
- X-ray (rarely used today)
Treatment for Appendicitis
The treatment is based on the involved severity and stage:
1. Antibiotics
Used to suppress infection and inflammation.
2. Appendectomy (Surgical Removal)
Gold-standard therapy:
- Laparoscopic (minimally invasive)
- Open surgery
3. Abscess Drainage
In case an abscess has developed it may require to be emptied before surgery.
4. Pain Management
Analgesics to reduce pain.
5. IV Fluids & Dietary Support
Applied as a hydrating and recovery agent.
Conclusion
Appendicitis is a severe illness which tends to occur in a relatively short span of time which results to life threatening crisis. Knowing the 4 stages of appendicitis, such as the first inflammation and the life-threatening perforation, the individuals would be informed of the symptoms early enough and seek urgent medical care. Early treatment and diagnostics of acute or chronic appendicitis plays a decisive role in the prevention of complications such as the development of an abscess, peritonitis or sepsis.
When facing unremitting right side abdominal pain, nausea or fever, medical examination is highly essential. Timely treatment will save lives as well as avoid the advanced and dangerous stages of the appendix.
You must be logged in to post a comment.